Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0, also known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution, is the current trend of automation and data exchange in manufacturing technologies. It includes cyber-physical systems, the Internet of Things, cloud computing and cognitive computing. These technologies are used to create smart factories, which are more efficient, productive, and flexible than traditional factories.!
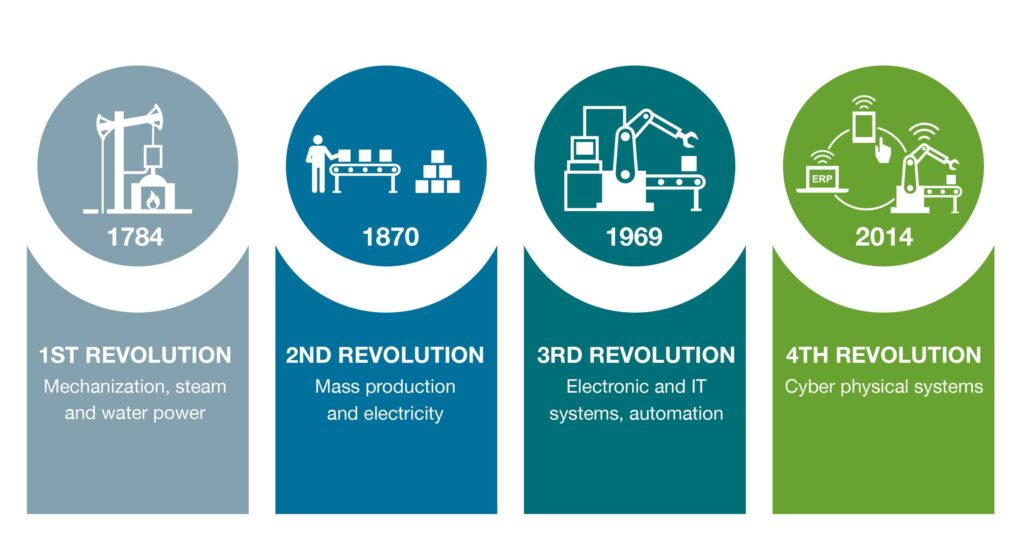
What is Industry 4.0 ?
- The term Industry 4.0 encompasses a promise of a new industrial revolution—one that marries advanced manufacturing techniques with the Internet of Things to create manufacturing systems that are not only interconnected, but communicate, analyze, and use information to drive further intelligent action back in the physical world.
- Industry 4.0 is disrupting the manufacturing on multiple fronts – from production throughput, maintenance and quality, to supply chain and inventory management.
- This disruption is significantly changing the mindset of the current industrial ecosystem, by the use of Industrial IOT and automation in the processes and systems has ushered a favorable transformation in the world of manufacturing.
- The basis for the fourth industrial revolution is the availability of all relevant information in the real time by connecting all instances involved in the value chain. The ability to derive the optimal value-added flow at any time from the data is also vital. The connection of people, things and systems create dynamic, self-organizing, real-time optimized value added connection within and across companies. These can be optimized according to different criteria such as costs, availability and consumption of resources.
“The Industry 4.0 train is leaving the station –Companies must decide when the best moment for them to hop on it”
COMPONENTS OF INDUSTRY 4.0
Sensors and IOT
Sensors and IOT can be installed inside/on machine and workstations to providing benefits such as :
- Direct and accurate information of the shop floors and industries.
- Better tracking of ongoing operations without the need of any personnel
- Real Time alerts of anomalies to prevent quality defects and machine/tool breakdowns
- Accurate monitoring of machines operational stats, planned preventive maintenance alerts.
Cloud Computing
- It brings the powers of new age technology of connecting everyone everywhere everytime to the industries.
- Maintaining and monitoring data over cloud servers provide even more ease than before to access information from anywhere at anytime
- Using cloud technologies, approvals and sharing reports setting targets becomes more easier.
- Remotely monitoring the industrial operations to ensure operational parameters are at optimal levels
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
- Data collected from shop floor, machines and various information systems like EMS, analysed and crunched using ML algorithms provide insights never available before.
- Artificial Intelligence methods provide predictive alerts and notifications on capacities and unforeseen wastages.
- Production Planning using ML and AI becomes more accurate and sustainable as system always keeps improvising from the live data being captured
Process Automations
- Using the powers of Industry 4.0, industrial processed such as production, inventory reconciliations, quality checks, dispatch ready checks, etc all can be replace by automated systems.
- Automated systems and operations ensures the sustainability of the optimal performance and standards as human errors are avoided and also systems in place keeps the instructed checks always in place.



EMPOWERING YOUR INDUSTRY THROUGH TECHNOLOGY
EMPOWER YOUR SHOP FLOOR
- Improve Overall Equipment Effectiveness and Manufacturing efficiency
- Ease in identifying Bottlenecks in operations
- Achieving Production optimization.
- Improve visibility through remote monitoring with real-time alerts.
- Enhancing Shop floor Communication through the “Go the Gemba”


ENSURING QUALITY
- Real-time monitoring alerts for Quality Checks.
- Transformation from Conventional Quality to Predictive Quality
- Improvising & Sustaining quality standards
EFFECTIVE & ON-TIME MAINTENANCE
- Transformation from Preventive Maintenance to Predictive Maintenance.
- Reducing unplanned downtime
- Improving machine optimal performance


TRACEABILITY OF INVENTORIES
- Real-time monitoring of available raw material & spare parts.
- Automated & Accurate reconciliations of inventories
- Tracking movement & utilization of raw material , components and finished goods.
- Ensuring smooth supply-chain through guided production planning systems
KEY BENEFITS OF INDUSTRY 4.0
IT EMPOWERS YOUR SHOP FLOOR
Accountability
Communication Gap & Delays will reduce
Performance accuracies & monitoring of team & individual
Sustainable process optimization & monitoring
Improve manufacturing efficiency
Reduce production waste for increased profits
Gain Real-time shop floor visibility
Alerts Shop-floor workers with instant notifications
Improve operator engagement and overall company communication.
Perfect Performance with TPM
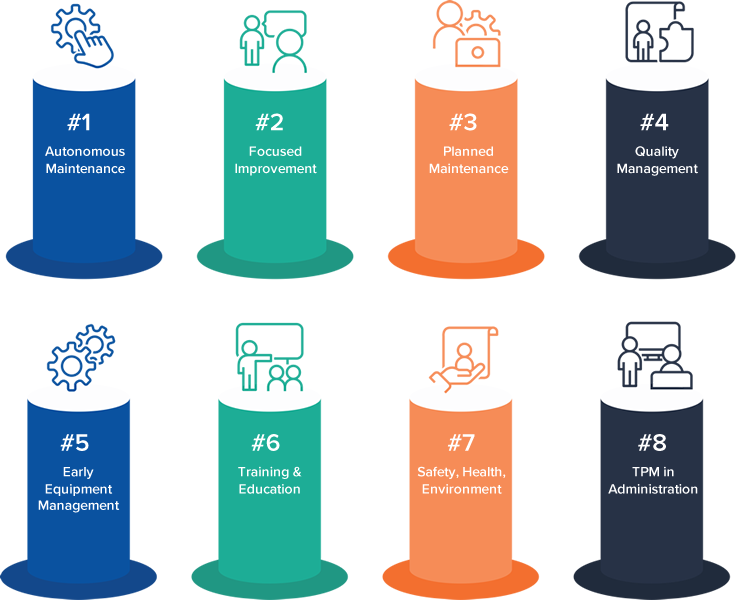

- TPM is a maintenance philosophy aimed at eliminating production losses due to equipment status, or in other words, keeping equipment in a position to produce at maximum capacity, the expected quality products, with no unscheduled stops.
- In a nutshell, Total Productive Maintenance is a system for optimizing maintenance and reaching a state of perfect efficiency in production.
The main goals of Total Productive Maintenance are
- No short stoppages or sub-optimal production rates
- No defects
- No unplanned downtime
- No accidents
- TPM proposes an 8-pillar approach that aims to cover every possible aspect of maintenance in the industrial manufacturing setting. These Pillars aim to eliminate the Six Big Losses.
With the emergence of Industry 4.0, this approach can be taken even further
- Predictive Maintenance by the means of Machine Learning implementing ‘Just in Time’ maintenance approach
- Predictive Quality real time data and Machine Learning help in performing focused Root Cause Analysis.
- Process Optimization maximizing production throughput by leveraging machine learning to prevent process disturbances
- Remote Monitoring get visibility into the equipment performance and actionable insights to maximize OEE
- Six Big Losses is a practical tool that can help identify inefficiencies in production.
- The approach focuses on losses, highlighting the idea that equipment-based flaws in the production workflow directly harm the bottom line of a manufacturing business.
- The Six Big Losses correspond to another well-known term coined by Nakajima – Overall Equipment Efficiency (OEE).
- The link between these two concepts is clear – deal with the six losses, and you’ll improve the OEE of your operation as a result.
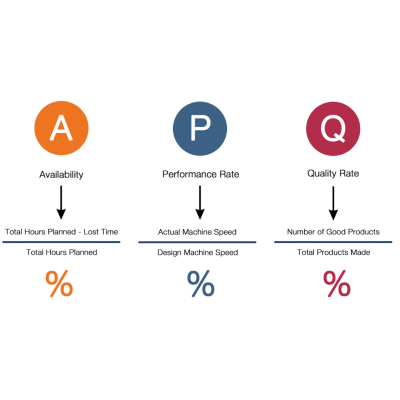
OVERALL EQUIPMENT EFFECTIVENESS
Overall equipment effectiveness is a measure of how well a manufacturing operation is utilized compared to its full potential, during the periods when it is scheduled to run. It identifies the percentage of manufacturing time that is truly productive.
An OEE score of 100% means you are manufacturing only Good Parts, as fast as possible, with no Stop Time
- In terms of OEE Good Parts means – 100 % Quality , As fast as possible means – 100 % Performance, No stop time means – 100 % Availability.
And these three factors i.e Availability , Performance , Quality takes into account a different types of Loss.
How does Overall Equipment Effectiveness help?
It provides a benchmark/baseline and a means to track progress in eliminating waste from a manufacturing process.

Availability Loss
Unplanned Stops that last a considerable amount of time during which equipment is scheduled to be running, but has stopped unexpectedly.
Planned Stops in which machinery is scheduled for production, but has ceased to run due to a planned stoppage.
Performance Loss
Small Stops in which machinery ceases to run for 1-2 minutes because of a problem that is typically resolved by the operator.
Reduced Speed is when equipment runs slower than the optimal cycle time (the least amount of time required to manufacture one item/volume unit.)
Quality Loss
Production Defects : Defective products manufactured while production is generally stable.
Startup Defects : Defects produced during the startup phase, before the normal production cycle is reached.

